2.3 KiB
User Guide
After the plugin is installed, create a new OpenStack environment.
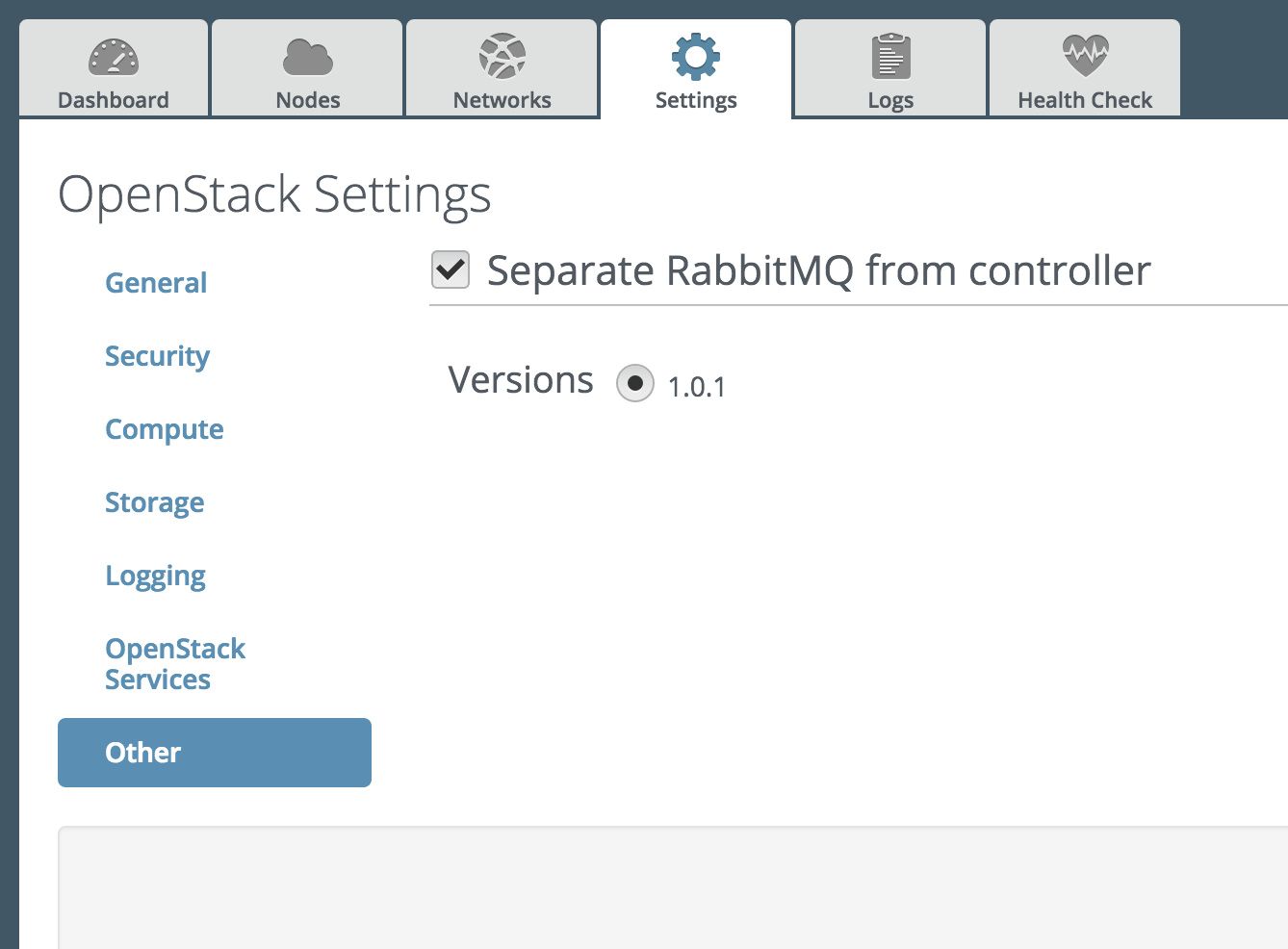
Open the Settings tab of the Fuel web UI and then select the Other menu. Select "Separate RabbitMQ from controller" checkbox. With the radio button below select the plugin version (multiple options are available only when several versions of the plugin are installed):
Go to the Nodes tab and here push Add Nodes button
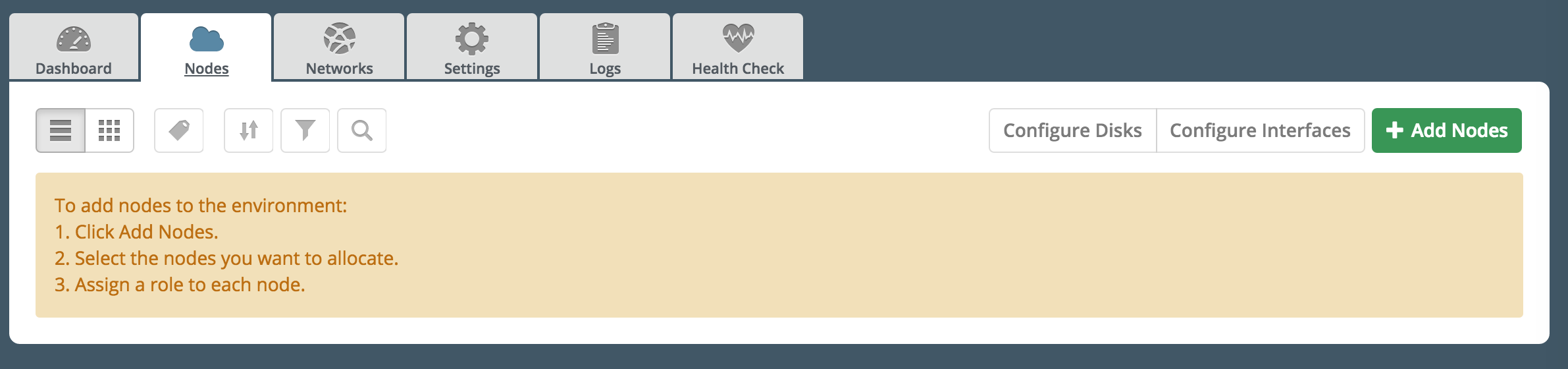
Note that now RabbitMQ role is available in the roles list.
Add nodes to the environment with RabbitMQ role assigned to some of them. On the screenshot below you may see environment with 1 controller, 1 compute and one RabbitMQ node. You can assign RabbitMQ role to more than one node.
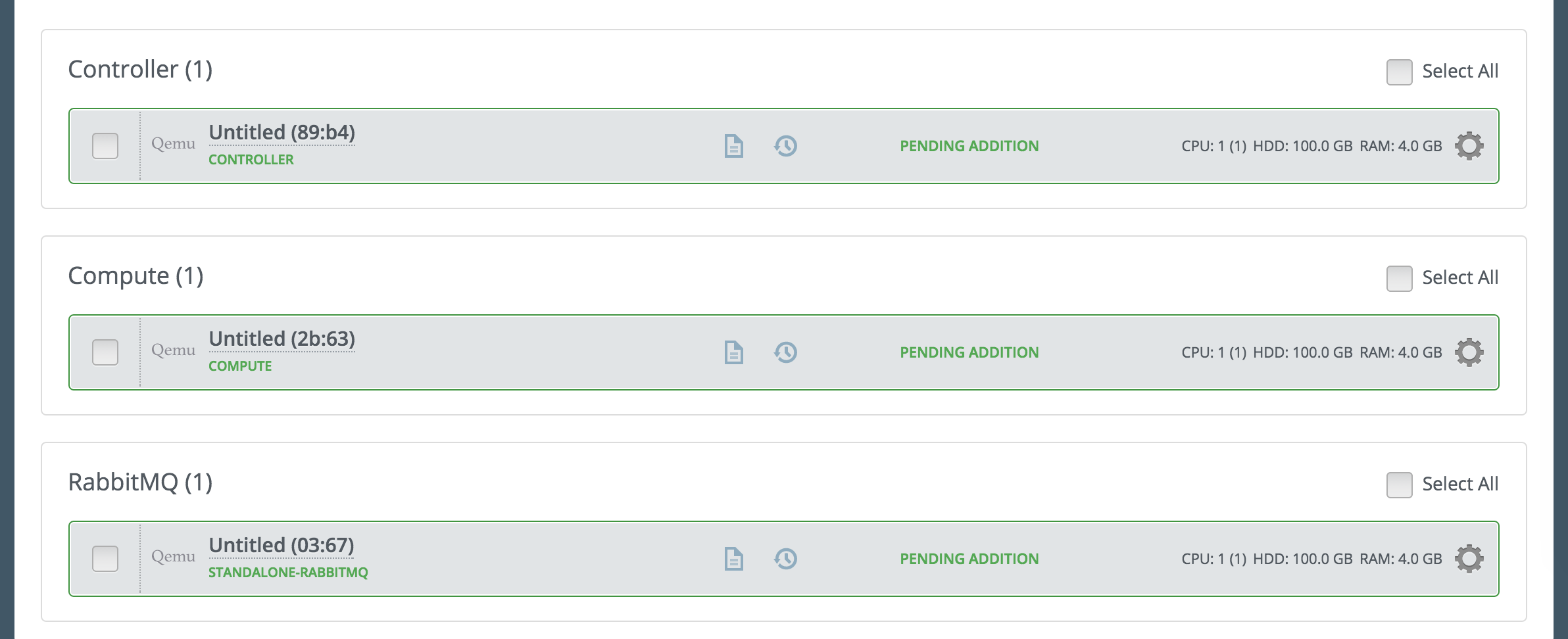
Finish configuring your environment.
How it works
Without the plugin, Fuel deploys RabbitMQ on Controller nodes. Here it is managed by Pacemaker along with a number of other processes.
With the plugin enabled, Fuel deployes RabbitMQ on dedicated nodes and here it is also managed by Pacemaker. But in that case RabbitMQ is not launched on the Controller nodes. Also note that two separate Pacemaker clusters are running on Controller and RabbitMQ nodes and they are not aware of each other.
- When the plugin is enabled, RabbitMQ log could be found in its regular place:
-
- on RabbitMQ node in /var/log/rabbitmq directory
- on master node in /var/log/remote/<node-name>/rabbitmq-*.log files
- The same applies to log of Pacemaker which manages RabbitMQ. Its location is:
-
- on RabbitMQ node /var/log/pacemaker.log
- on master node in the following files:
- /var/log/remote/<node-name>/attrd.log
- /var/log/remote/<node-name>/crmd.log
- /var/log/remote/<node-name>/cib.log
- /var/log/remote/<node-name>/lrmd.log
- /var/log/remote/<node-name>/pengine.log