3.6 KiB
User Guide
Creating Cinder volume
To verify that EMC VNX plugin is properly installed, you should create a Cinder volume and attach it to a newly created VM using for example OpenStack CLI tools.
Create a Cinder volume. In this example, a 10GB volume was created using cinder create <volume size> command:
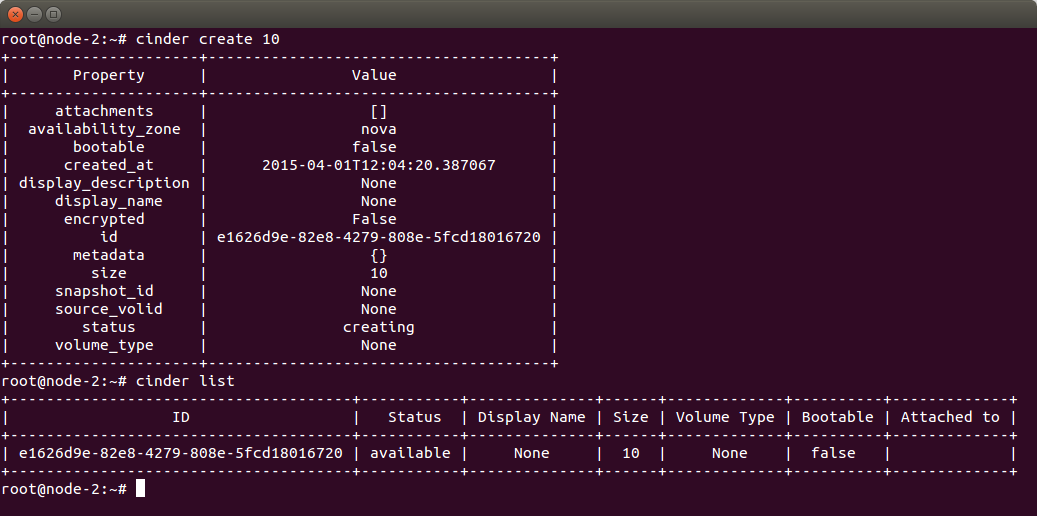
Using cinder list command (see the screenshot above), let’s check if the volume was created. The output provides information on ID, Status (it’s available), Size (10) and some other parameters.
Now you can see how it looks on the EMC VNX. In the example environment, EMC VNX SP has 192.168.200.30 IP address. Before you do this, add /opt/Navisphere/bin directory to PATH environment variable using export PATH=$PATH:/opt/Navisphere/bin command and save your EMC credentials using naviseccli -addusersecurity -password <password> -scope 0 -user <username> command to simplify syntax in succeeding naviseccli commands.
Use naviseccli -h <SP IP> lun -list command to list LUNs created on the EMC:
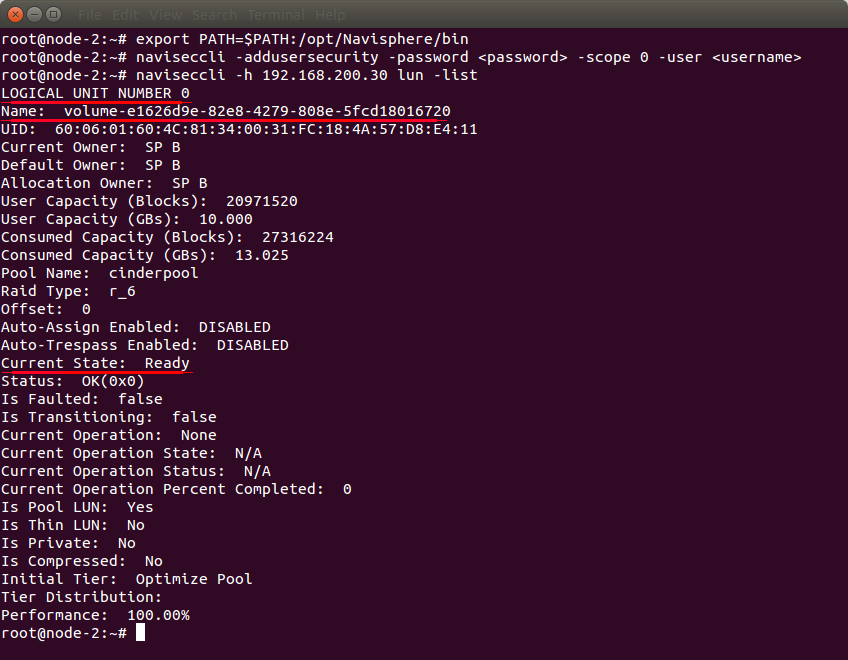
In the given example there is one LUN with ID: 0, name: volume-e1626d9e-82e8-4279-808e-5fcd18016720 (naming schema is “volume-<Cinder volume id>”) and it is in “Ready” state, so everything is fine.
Now create a new VM. To do this, you have to know IDs of a glance image (use glance image-list command) and a network (use nova net-list command):
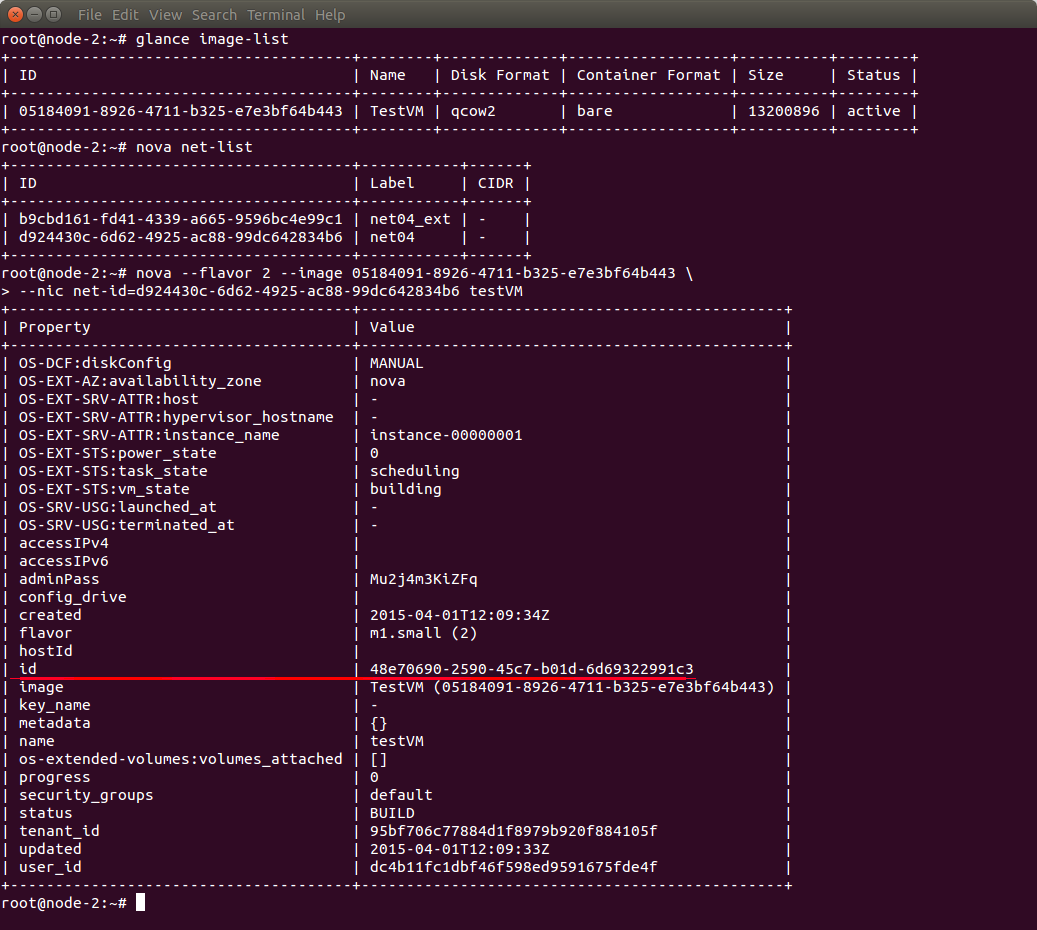
Note the VM’s ID which is 48e70690-2590-45c7-b01d-6d69322991c3 in the given example.
Show details of the new VM to check its state and to see on which node it has been created (use nova show <id> command). In the output, we see that the VM is running on the node-3 and it is active:

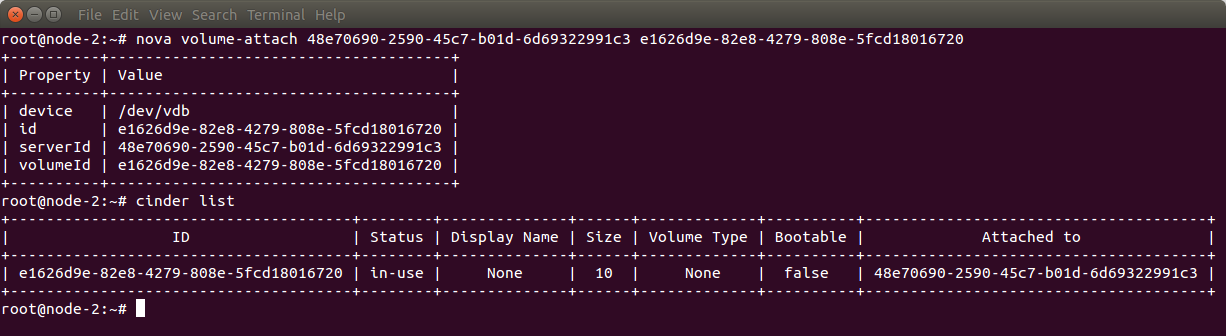
Attach the Cinder volume to the VM (use nova volume-attach <VM id> <volume id>) and verify using cinder list command:
To list storage groups configured on EMC VNX, use naviseccli -h <SP IP> storagegroup -list command:

There is one “node-3” storage group with one LUN attached. The LUN has local ID 0 (ALU Number) and it is available as LUN 133 (HLU Number) for the node-3. There are four iSCSI HBA/SP Pairs - one per the SP-Port pair.
You can also check if iSCSI sessions are active using naviseccli -h <SP IP> port -list -hba command:
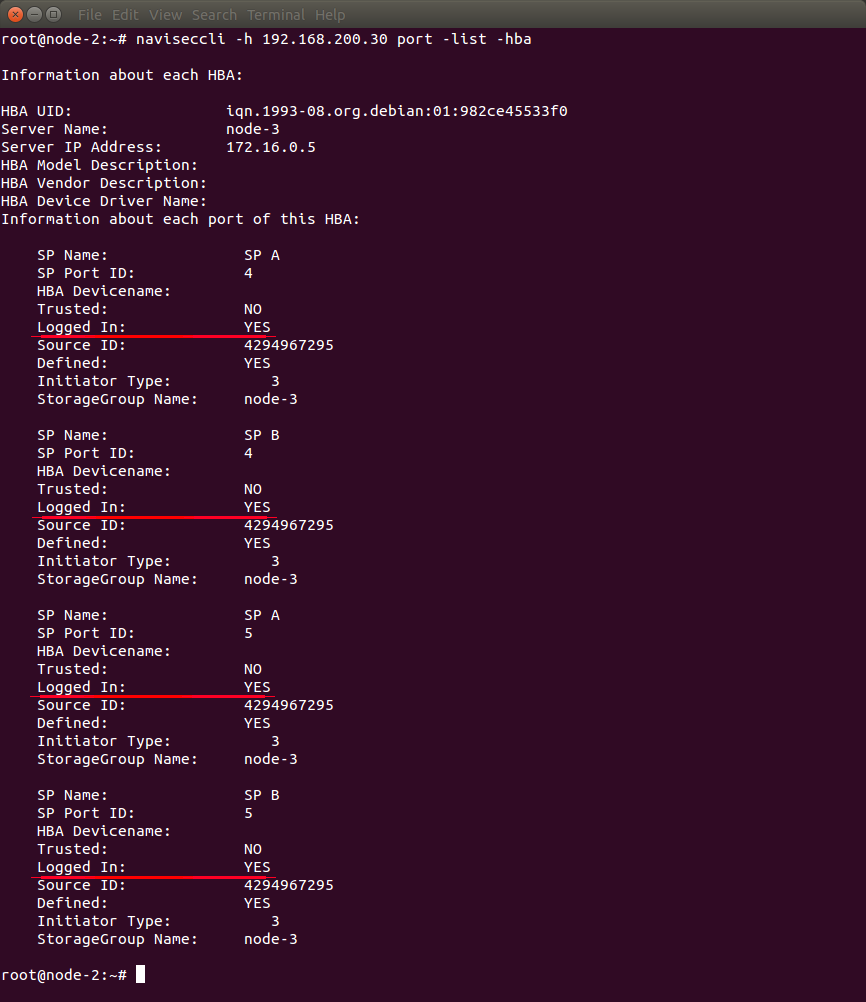
Look at “Logged In” parameter of each port. In the given example, all four sessions are active (in the output, it looks like Logged In: YES).
When you log into the node-3 node, you can verify the following; if iSCSI sessions are active using iscsiadm -m session command, if a multipath device has been created by multipath daemon using multipath -ll command, if VM is using the multipath device using lsof -n -p `pgrep -f <VM id>` | grep /dev/<DM device name> command:
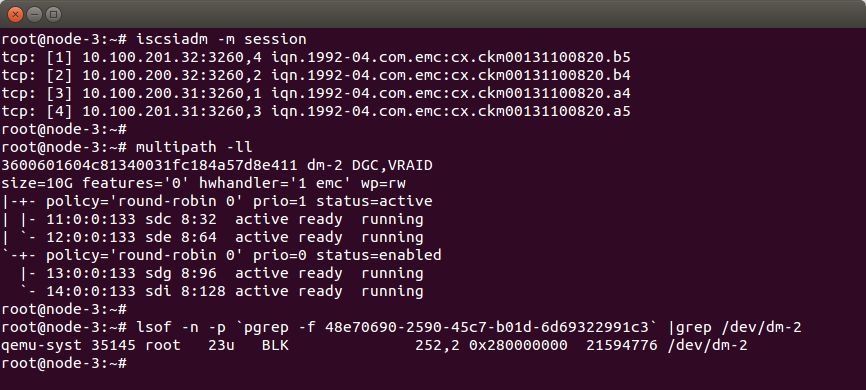
In the example, there are four active sessions (the same as on the EMC) and the multipath device dm-2 has been created. The multipath device has four paths and all are running (each one per iSCSI session). In the output of the third command, you can see that qemu is using /dev/dm-2 multipath device, so everything is fine.